Converting Int to Float or Float to Int using Bitwise operations (software floating point)
First, a paper you should consider reading, if you want to understand floating point foibles better: "What Every Computer Scientist Should Know About Floating Point Arithmetic," http://www.validlab.com/goldberg/paper.pdf
And now to some meat.
The following code is bare bones, and attempts to produce an IEEE-754 single precision float from an unsigned int in the range 0 < value < 224. That's the format you're most likely to encounter on modern hardware, and it's the format you seem to reference in your original question.
IEEE-754 single-precision floats are divided into three fields: A single sign bit, 8 bits of exponent, and 23 bits of significand (sometimes called a mantissa). IEEE-754 uses a hidden 1 significand, meaning that the significand is actually 24 bits total. The bits are packed left to right, with the sign bit in bit 31, exponent in bits 30 .. 23, and the significand in bits 22 .. 0. The following diagram from Wikipedia illustrates:
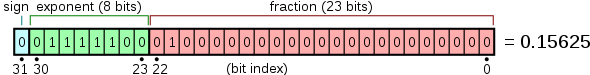
The exponent has a bias of 127, meaning that the actual exponent associated with the floating point number is 127 less than the value stored in the exponent field. An exponent of 0 therefore would be encoded as 127.
(Note: The full Wikipedia article may be interesting to you. Ref: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_precision_floating-point_format )
Therefore, the IEEE-754 number 0x40000000 is interpreted as follows:
- Bit 31 = 0: Positive value
- Bits 30 .. 23 = 0x80: Exponent = 128 - 127 = 1 (aka. 21)
- Bits 22 .. 0 are all 0: Significand = 1.00000000_00000000_0000000. (Note I restored the hidden 1).
So the value is 1.0 x 21 = 2.0.
To convert an unsigned int in the limited range given above, then, to something in IEEE-754 format, you might use a function like the one below. It takes the following steps:
- Aligns the leading 1 of the integer to the position of the hidden 1 in the floating point representation.
- While aligning the integer, records the total number of shifts made.
- Masks away the hidden 1.
- Using the number of shifts made, computes the exponent and appends it to the number.
- Using
reinterpret_cast, converts the resulting bit-pattern to afloat. This part is an ugly hack, because it uses a type-punned pointer. You could also do this by abusing aunion. Some platforms provide an intrinsic operation (such as_itof) to make this reinterpretation less ugly.
There are much faster ways to do this; this one is meant to be pedagogically useful, if not super efficient:
float uint_to_float(unsigned int significand)
{
// Only support 0 < significand < 1 << 24.
if (significand == 0 || significand >= 1 << 24)
return -1.0; // or abort(); or whatever you'd like here.
int shifts = 0;
// Align the leading 1 of the significand to the hidden-1
// position. Count the number of shifts required.
while ((significand & (1 << 23)) == 0)
{
significand <<= 1;
shifts++;
}
// The number 1.0 has an exponent of 0, and would need to be
// shifted left 23 times. The number 2.0, however, has an
// exponent of 1 and needs to be shifted left only 22 times.
// Therefore, the exponent should be (23 - shifts). IEEE-754
// format requires a bias of 127, though, so the exponent field
// is given by the following expression:
unsigned int exponent = 127 + 23 - shifts;
// Now merge significand and exponent. Be sure to strip away
// the hidden 1 in the significand.
unsigned int merged = (exponent << 23) | (significand & 0x7FFFFF);
// Reinterpret as a float and return. This is an evil hack.
return *reinterpret_cast< float* >( &merged );
}
You can make this process more efficient using functions that detect the leading 1 in a number. (These sometimes go by names like clz for "count leading zeros", or norm for "normalize".)
You can also extend this to signed numbers by recording the sign, taking the absolute value of the integer, performing the steps above, and then putting the sign into bit 31 of the number.
For integers >= 224, the entire integer does not fit into the significand field of the 32-bit float format. This is why you need to "round": You lose LSBs in order to make the value fit. Thus, multiple integers will end up mapping to the same floating point pattern. The exact mapping depends on the rounding mode (round toward -Inf, round toward +Inf, round toward zero, round toward nearest even). But the fact of the matter is you can't shove 24 bits into fewer than 24 bits without some loss.
You can see this in terms of the code above. It works by aligning the leading 1 to the hidden 1 position. If a value was >= 224, the code would need to shift right, not left, and that necessarily shifts LSBs away. Rounding modes just tell you how to handle the bits shifted away.
Have you checked the IEEE 754 floating-point representation?
In 32-bit normalized form, it has (mantissa's) sign bit, 8-bit exponent (excess-127, I think) and 23-bit mantissa in "decimal" except that the "0." is dropped (always in that form) and the radix is 2, not 10. That is: the MSB value is 1/2, the next bit 1/4 and so on.
Joe Z's answer is elegant but range of input values is highly limited. 32 bit float can store all integer values from the following range:
[-224...+224] = [-16777216...+16777216]
and some other values outside this range.
The whole range would be covered by this:
float int2float(int value)
{
// handles all values from [-2^24...2^24]
// outside this range only some integers may be represented exactly
// this method will use truncation 'rounding mode' during conversion
// we can safely reinterpret it as 0.0
if (value == 0) return 0.0;
if (value == (1U<<31)) // ie -2^31
{
// -(-2^31) = -2^31 so we'll not be able to handle it below - use const
// value = 0xCF000000;
return (float)INT_MIN; // *((float*)&value); is undefined behaviour
}
int sign = 0;
// handle negative values
if (value < 0)
{
sign = 1U << 31;
value = -value;
}
// although right shift of signed is undefined - all compilers (that I know) do
// arithmetic shift (copies sign into MSB) is what I prefer here
// hence using unsigned abs_value_copy for shift
unsigned int abs_value_copy = value;
// find leading one
int bit_num = 31;
int shift_count = 0;
for(; bit_num > 0; bit_num--)
{
if (abs_value_copy & (1U<<bit_num))
{
if (bit_num >= 23)
{
// need to shift right
shift_count = bit_num - 23;
abs_value_copy >>= shift_count;
}
else
{
// need to shift left
shift_count = 23 - bit_num;
abs_value_copy <<= shift_count;
}
break;
}
}
// exponent is biased by 127
int exp = bit_num + 127;
// clear leading 1 (bit #23) (it will implicitly be there but not stored)
int coeff = abs_value_copy & ~(1<<23);
// move exp to the right place
exp <<= 23;
union
{
int rint;
float rfloat;
}ret = { sign | exp | coeff };
return ret.rfloat;
}
Of course there are other means to find abs value of int (branchless). Similarly couting leading zeros can also be done without a branch so treat this example as example ;-).