Legendre Polynomial Integral over half space
Integration of Equation (34) in MathWorld gives the integral $I_{nm}$ as a sum $$I_{nm}=\sum _{q=0}^m \frac{2^{-q}}{q+1} \binom{-m-1}{q} \binom{m}{q} \, _3F_2\left(-n,n+1,q+1;1,q+2;\tfrac{1}{2}\right).$$
As noted by the OP, Mathworld also gives the explicit expression:
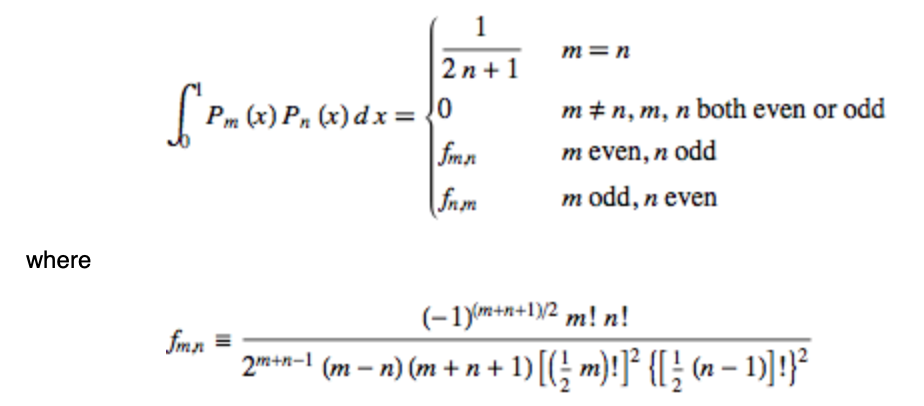
I found the following answer, based on the idea by
Dougall, John, The product of two Legendre polynomials, Proc. Glasg. Math. Assoc. 1, 121-125 (1953). ZBL0052.06404.
Expand the product in Legendre basis $$ P_n(x) P_m(x) = \sum_{k=0}^l A_{2k} P_{2l+1-2k}(x) \\ \quad \text{for} \quad A_{2k} = \frac{4(l-k)+3}{2(2l-k)+3} \frac{\lambda_k \lambda_{n-k} \lambda_{m-k}}{\lambda_{2l+1-k}} \,, \lambda_k = \frac{(2k)!}{2^{n+1} n!} \,. $$ Integration is now trivial $$ I_{n,m} = \sum_{k=0}^l A_{2k} \int_0^1 P_{2l+1-2k}(x) \, \mathrm{d}x \\ \int_0^1 P_{2p+1}(x) \, \mathrm{d}x = \frac{(-1)^p}{4^{p+1}} \frac{(2p)!}{(p!)^2} \frac{2}{p+1} $$