Python Progress Bar
Use alive-progress, the coolest progress bar ever!

To use any progress bar framework in a useful manner, i.e. to get a percentage of completion and an estimated time of arrival (ETA), you need to be able to tell how many steps your processing will have.
Then you can just insert an yield to mark an item has been processed, and you're good to go!
def compute():
for i in range(1000):
... # process items as usual.
yield # insert this :)
Then just use it like:
from alive_progress import alive_bar
with alive_bar(1000) as bar:
for i in compute():
bar()
To get an awesome and alive progress bar!
|█████████████▎ | ▅▃▁ 321/1000 [32%] in 8s (40.1/s, eta: 16s)
Disclosure: I'm the author of alive-progress, but it should solve your problem nicely! Read the documentation at https://github.com/rsalmei/alive-progress to know more. Now it works also on Jupyter Notebooks! Here are some more examples of what it can do:


With tqdm (conda install tqdm or pip install tqdm) you can add a progress meter to your loops in a second:
from time import sleep
from tqdm import tqdm
for i in tqdm(range(10)):
sleep(3)
60%|██████ | 6/10 [00:18<00:12, 0.33 it/s]
Also, there is a notebook version:
from tqdm.notebook import tqdm
for i in tqdm(range(100)):
sleep(3)
You can use tqdm.auto instead of tqdm.notebook to work in both a terminal and notebooks.
tqdm.contrib contains some helper functions to do things like enumerate, map, and zip. There are concurrent maps in tqdm.contrib.concurrent.
You can even get progress sent to your phone after disconnecting from a jupyter notebook using tqdm.contrib.telegram or tqdm.contrib.discord.
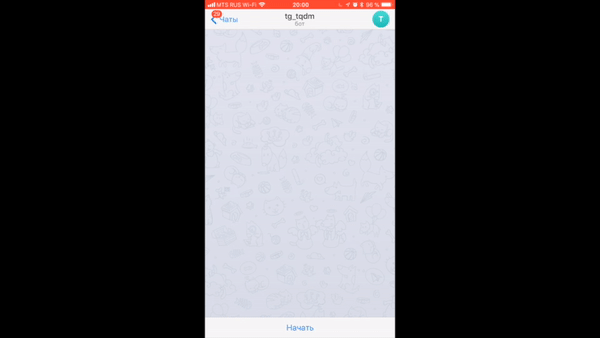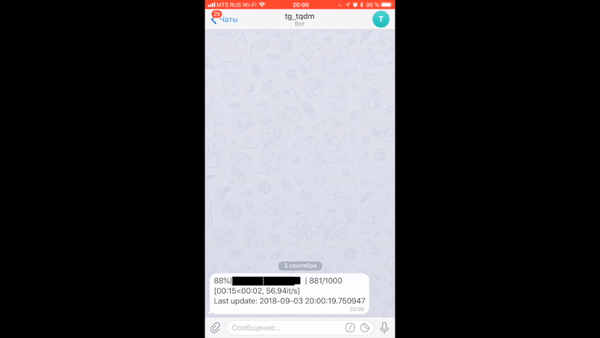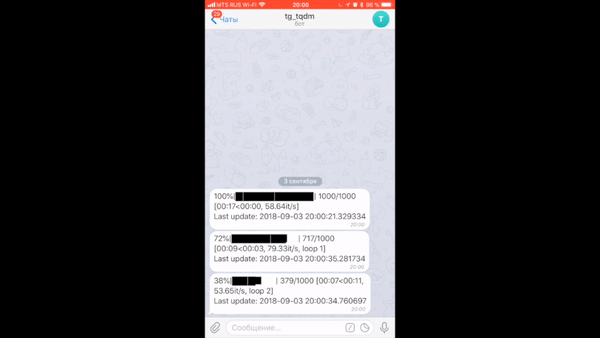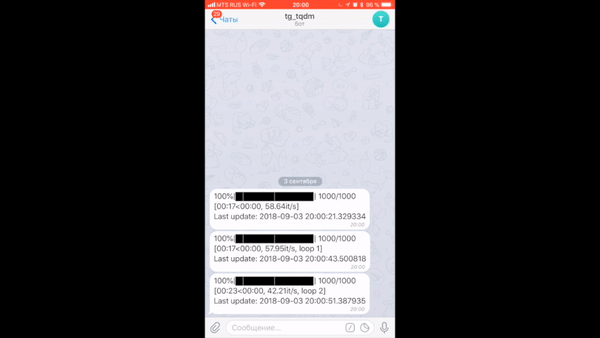
There are specific libraries (like this one here) but maybe something very simple would do:
import time
import sys
toolbar_width = 40
# setup toolbar
sys.stdout.write("[%s]" % (" " * toolbar_width))
sys.stdout.flush()
sys.stdout.write("\b" * (toolbar_width+1)) # return to start of line, after '['
for i in xrange(toolbar_width):
time.sleep(0.1) # do real work here
# update the bar
sys.stdout.write("-")
sys.stdout.flush()
sys.stdout.write("]\n") # this ends the progress bar
Note: progressbar2 is a fork of progressbar which hasn't been maintained in years.